
RAG Evaluation Framework for Production AI Systems
Author:
Jake Meany (Director of Marketing, LayerLens)
Last updated:
Jan 16, 2026
Published:
Jan 16, 2026
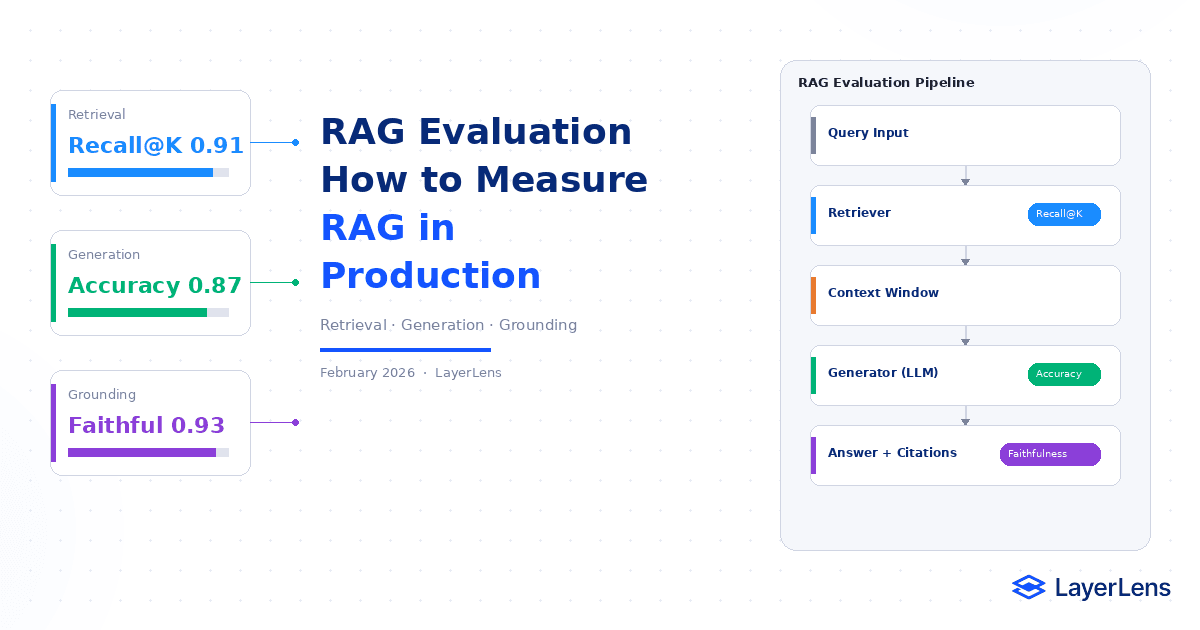
RAG evaluation separates retrieval, generation, and grounding performance.
End-to-end accuracy alone hides where failure occurs.
Core rag evaluation metrics include Recall@K, Precision@K, ranking quality, answer correctness, and faithfulness.
Composite scores summarize system health but do not replace decomposed monitoring.
Production RAG systems require drift detection, instrumentation, and governance thresholds.
Why RAG evaluation feels confusing in practice
RAG systems introduce two separate sources of uncertainty: retrieval and generation. Retrieval can miss relevant documents. Generation can produce fluent but unsupported answers. When both behaviors collapse into a single accuracy number, debugging becomes guesswork.
RAG evaluation metrics separate those signals. Instead of “answers seem worse,” you see whether retrieval recall fell, ranking degraded, or faithfulness declined. That separation turns diagnosis from intuition into measurement.
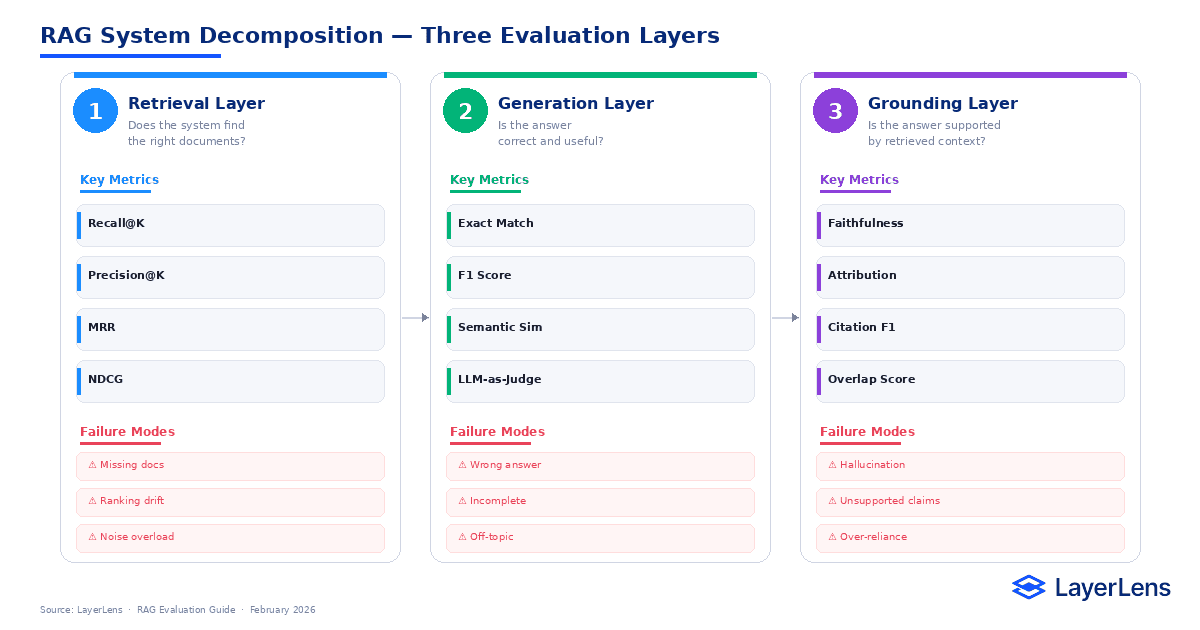
Retrieval, generation, and grounding operate as distinct evaluation layers.
What Is RAG Evaluation?
RAG evaluation measures performance across three separable layers:
Retrieval quality
Generation correctness
Grounding fidelity
Each layer uses different rag evaluation metrics. Combining them prematurely obscures root cause.
Retrieval-grounded generation research supports decomposed evaluation for identifying error sources (retrieval-grounded generation research).
Why Evaluate RAG in Layers?
A RAG pipeline contains at least two models: a retriever and a generator.
If retrieval fails, the generator never sees the right information.
If retrieval succeeds but generation misuses context, the error is generative.
If both succeed but unsupported claims appear, the issue is grounding.
Different failures require different corrections. Layered evaluation exposes which component needs intervention.
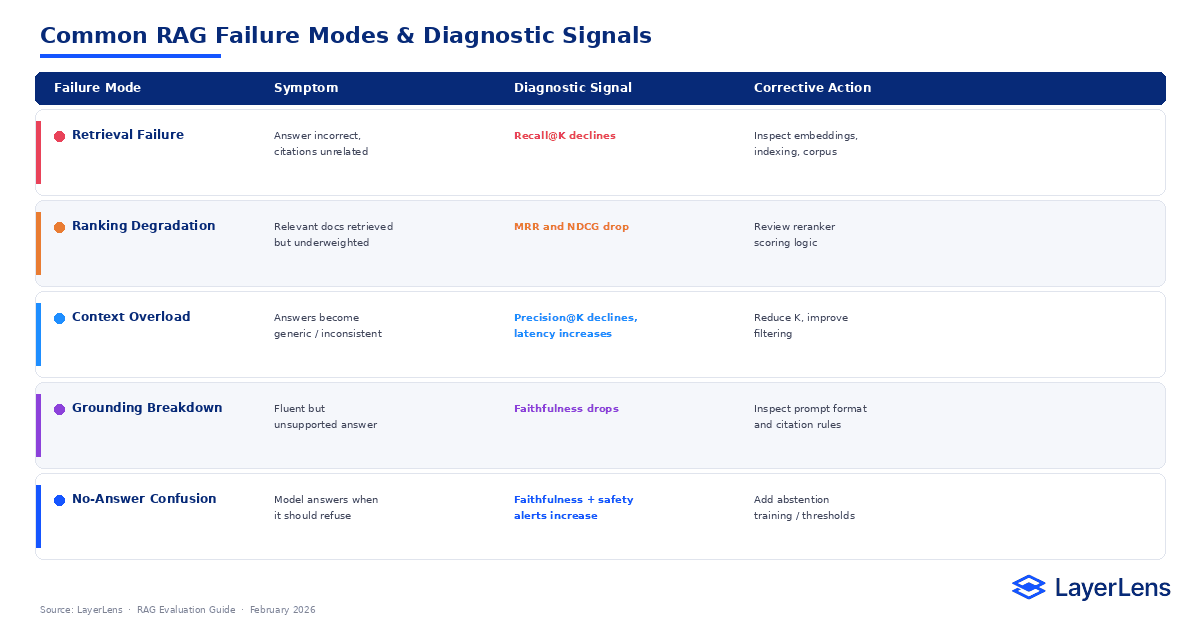
What Are Common RAG Failure Modes?
RAG systems tend to fail in recognizable patterns.
Retrieval failure
Symptom: answer incorrect, citations unrelated
Signal: Recall@K declines
Ranking degradation
Symptom: relevant documents retrieved but underweighted
Signal: MRR and NDCG drop
Context overload
Symptom: answers become generic or inconsistent
Signal: Precision@K declines, latency increases
Grounding breakdown
Symptom: fluent but unsupported answer
Signal: Faithfulness drops
No-answer confusion
Symptom: model answers when it should refuse
Signal: Faithfulness and safety alerts increase
These patterns narrow the search space for debugging.
What Are the Key RAG Evaluation Metrics for Retrieval?
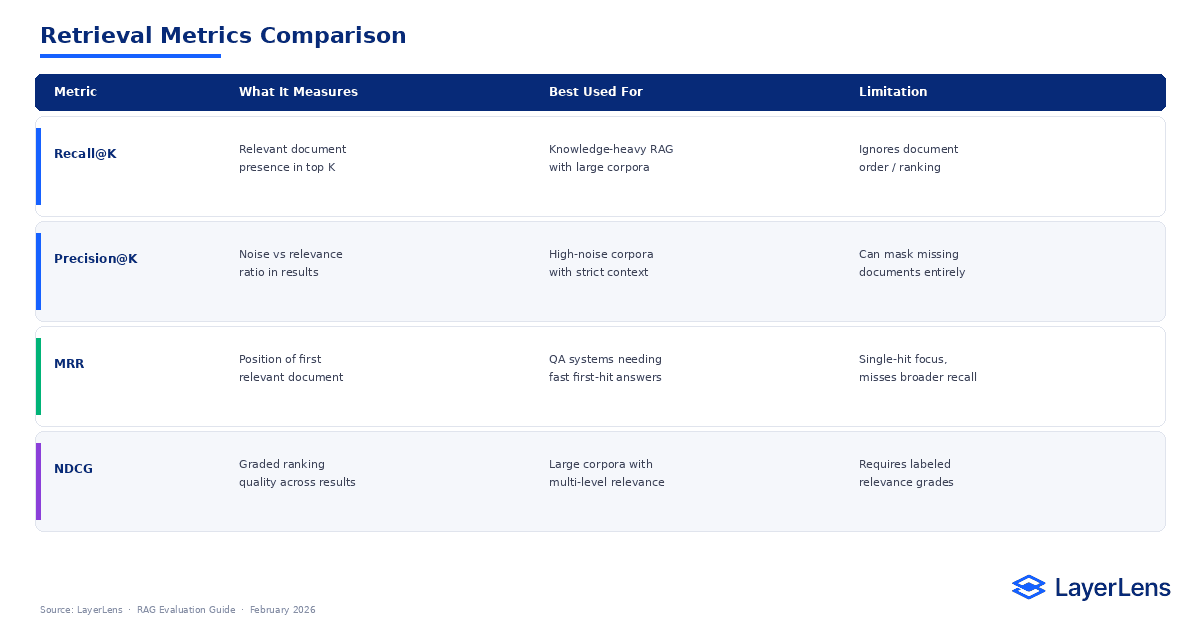
Recall@K
Indicates whether relevant documents appear within the top K results.
Precision@K
Indicates the proportion of relevant documents in retrieved results.
Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR)
Captures how early the first relevant document appears.
Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG)
Measures ranking quality with graded relevance weighting.
How to think about retrieval metrics:
Recall tells you if the right content is present.
Precision tells you if noise is polluting the context.
MRR tells you if the relevant content appears early enough to matter.
NDCG tells you whether ranking quality holds beyond binary relevance.
In practice, ranking drift often precedes recall collapse.
How Do Retrieval Metrics Compare?
LayerLens benchmark coverage includes retrieval-focused evaluation categories (LayerLens benchmark coverage).
How Do You Measure RAG Generation Quality?
End-to-End Accuracy
Measures whether the final answer is correct.
Exact Match / F1
Useful when deterministic answers exist.
Semantic Similarity
Captures meaning alignment when strict matching fails.
For a deeper look at generation-side metrics including semantic similarity and LLM-as-judge scoring, see LLM Evaluation Metrics That Actually Matter in Production (add link when live).
How Is Faithfulness Measured?
Faithfulness measures whether answers are supported by retrieved documents.
An answer may be correct but unsupported. In compliance-sensitive environments, unsupported correctness still carries risk.
Common approaches:
Reference overlap
Evidence attribution
LLM-as-judge grounding checks (LLM-as-judge research)
Faithfulness should not be treated as secondary; it often determines trust.
How Do You Combine RAG Evaluation Metrics?
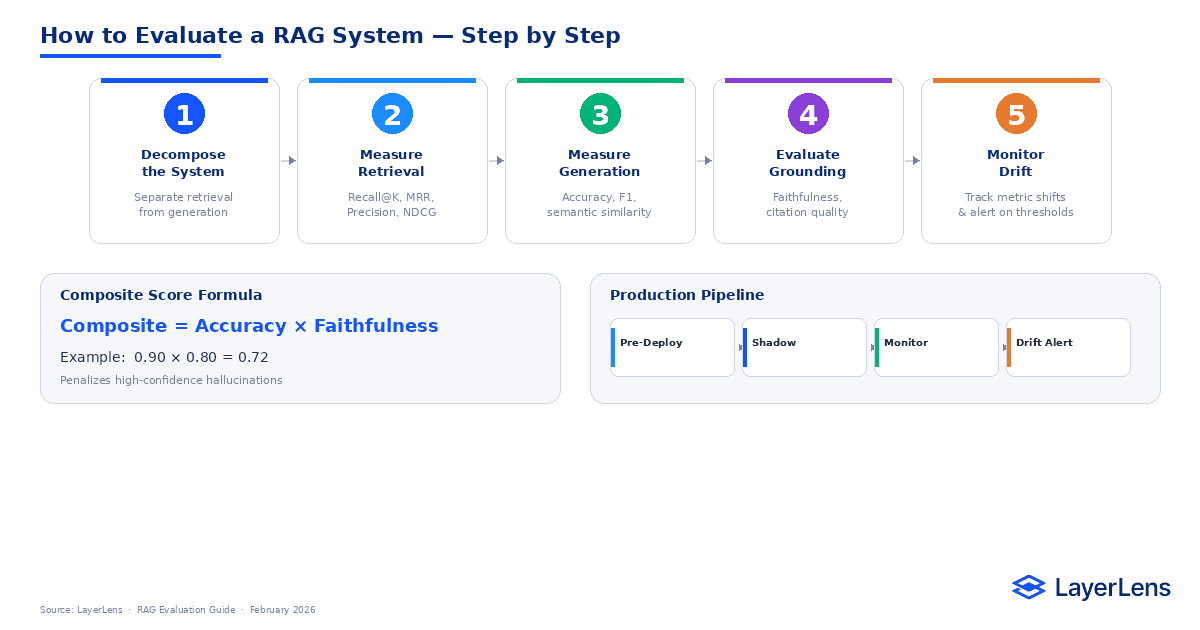
Composite Score = End-to-End Accuracy × Faithfulness
If accuracy is 0.90 and faithfulness is 0.80, composite = 0.72.
Multiplication discourages high-confidence hallucinations. Composite scores summarize performance but do not replace decomposed monitoring.
Compare RAG-capable systems using LayerLens comparison dashboards (LayerLens comparison dashboards).
How to Evaluate a RAG System Step-by-Step
Decompose the system
Separate retrieval from generation to localize failures.
Measure retrieval metrics
Evaluate Recall@K, Precision@K, MRR, and NDCG on representative queries.
Measure generation quality
Assess answer correctness and semantic alignment.
Evaluate grounding
Confirm answers are supported by retrieved context.
Monitor drift
Track metric movement over time and alert on threshold breaches.
For a broader framework covering evaluation infrastructure beyond RAG, see How to Build an LLM Evaluation Framework (Enterprise Playbook).
How Should You Build a Production RAG Evaluation Pipeline?
Pre-Deployment
Measure retrieval and generation metrics against domain datasets and enforce defined thresholds.
Shadow Deployment
Route live traffic without exposure to establish baseline performance and detect distribution shift (distribution shift research).
Continuous Monitoring
Track retrieval recall, faithfulness violations, latency distribution, and cost per request.
Drift Detection
Detect statistical changes in retrieval quality and answer grounding over time.
LayerLens evaluation dashboards provide structured production monitoring (LayerLens evaluation dashboards).
What Should You Do When RAG Metrics Degrade?
Recall declines → inspect embeddings, indexing, or corpus changes.
Ranking drops → review reranker scoring.
Faithfulness declines → inspect prompt format and citation rules.
Accuracy declines while retrieval stable → check corpus freshness.
Decomposition guides corrective action.
Conclusion: Retrieval Is Half the System
RAG evaluation works when retrieval, generation, and grounding are measured independently. Composite scores summarize performance, but separation enables control.
Production systems improve when evaluation isolates failure surfaces early and links metrics to operational decisions.
Retrieval is not preprocessing. It determines whether the model has a chance to succeed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important metric for RAG evaluation?
No single metric suffices. Retrieval recall, answer correctness, and faithfulness must be measured together.
Why is faithfulness important?
It ensures answers are grounded in retrieved documents and reduces hallucination risk.
How often should RAG systems be evaluated?
Continuously in production with drift detection enabled.
What is the difference between Recall@K and Precision@K?
Recall@K measures whether relevant documents are retrieved; Precision@K measures how many retrieved documents are relevant.
How do you detect retrieval drift?
Monitor changes in Recall@K, ranking metrics, and query distribution over time.
Key Takeaways
Effective rag evaluation:
Separates retrieval and generation
Measures ranking quality
Tracks grounding fidelity
Monitors drift continuously
Connects metrics to deployment thresholds