
LLM Hallucination Detection in Production
Author:
Jake Meany (Director of Marketing, LayerLens)
Last updated:
Feb 13, 2026
Published:
Feb 13, 2026
LLM hallucination detection in production is probabilistic and multi-surface.
Fabrication, citation drift, speculative completion, and agentic execution errors require distinct detection logic.
Faithfulness scoring and entailment models reduce risk but introduce calibration tradeoffs.
Retrieval systems and agentic workflows expand hallucination surfaces beyond simple fabrication.
Combining evaluation, observability, mitigation strategies, and tooling reduces operational hallucination risk.
A model answers correctly and cites the wrong source.
The statement is true. The reference is fabricated.
In most dashboards, this passes.
LLM hallucination detection is not about catching obvious inventions. It is about identifying unsupported claims, misplaced certainty, and subtle grounding failures that survive surface-level evaluation.
The industry definition of hallucination as “making things up” is incomplete. The harder problem is determining when a model’s output is not supported by available evidence, even if it appears plausible.
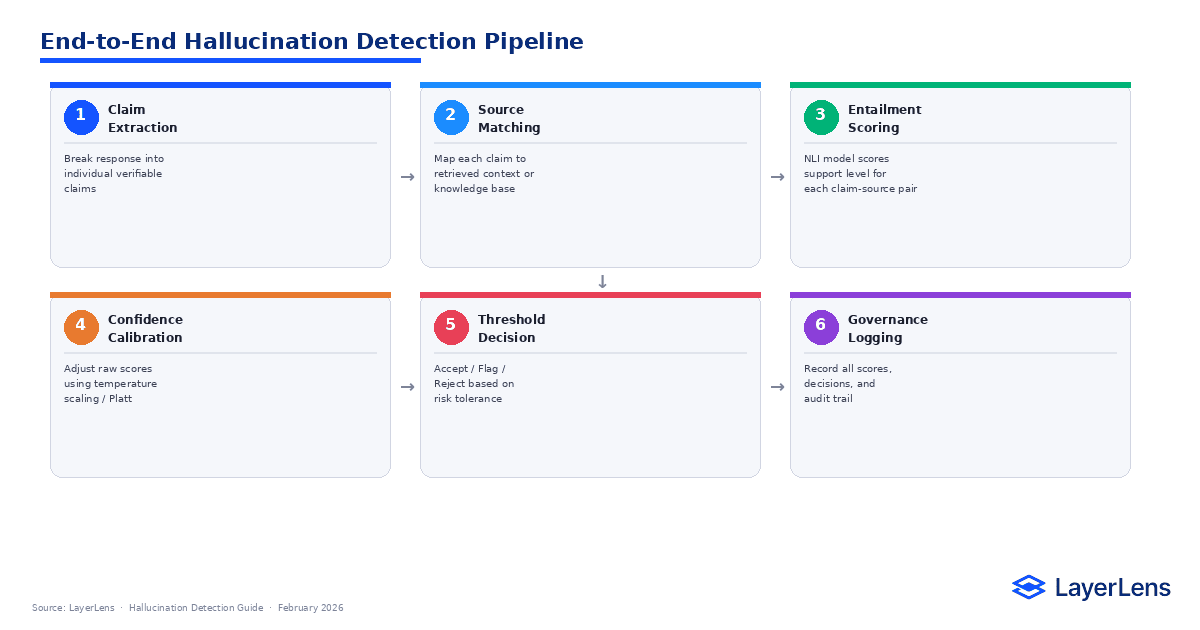
What Are the Different Types of LLM Hallucinations?
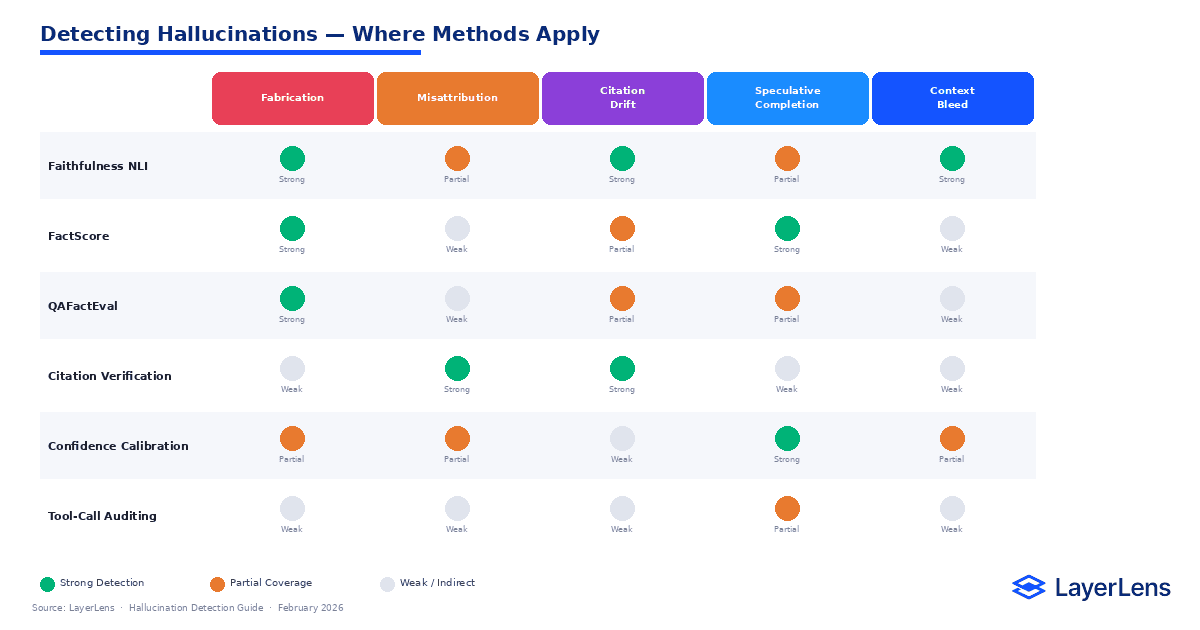
LLM hallucination detection must begin with taxonomy clarity. Not all hallucinations are identical.
Fabrication
The model generates content not grounded in training distribution or provided context.
Misattribution
The model produces a correct statement but assigns it to the wrong source or entity.
Citation Drift
Common in retrieval systems. The answer is grounded in retrieved material, but the cited sentence does not support the claim. For retrieval-grounded evaluation details, see RAG evaluation in production (https://layerlens.ai/blog/rag-evaluation).
Speculative Completion
The model fills underspecified prompts with plausible but unverified content.
Context Bleed
Information from earlier turns contaminates later responses in ways that are not supported by current input.
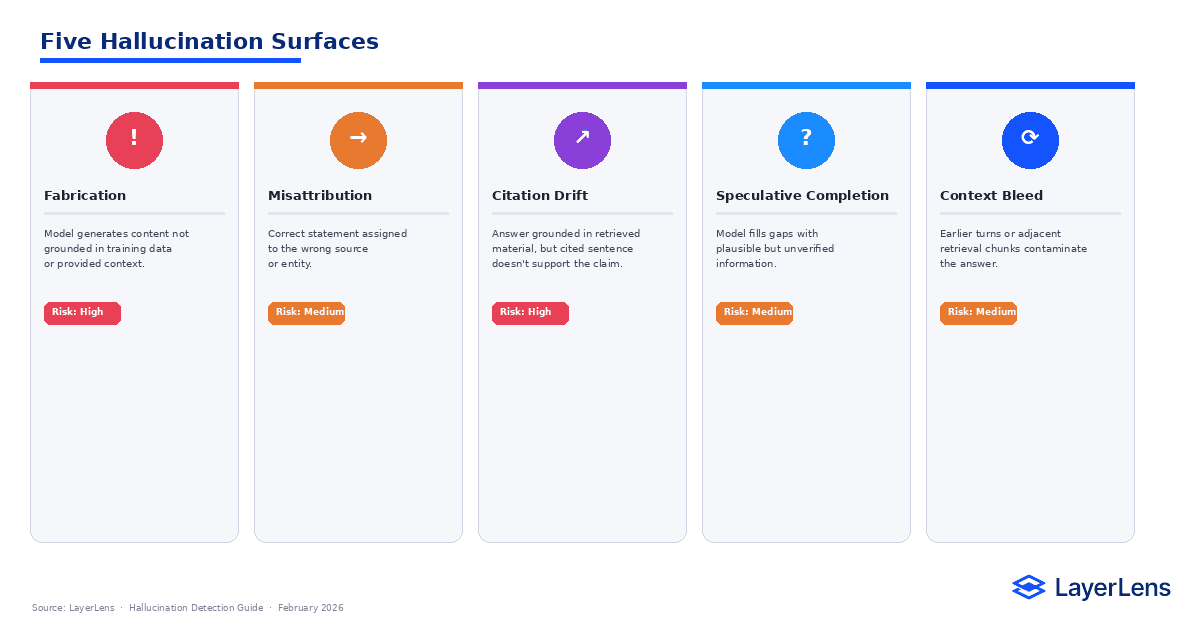
Each surface requires distinct detection strategies. Treating hallucination detection as a single binary classification collapses nuance.
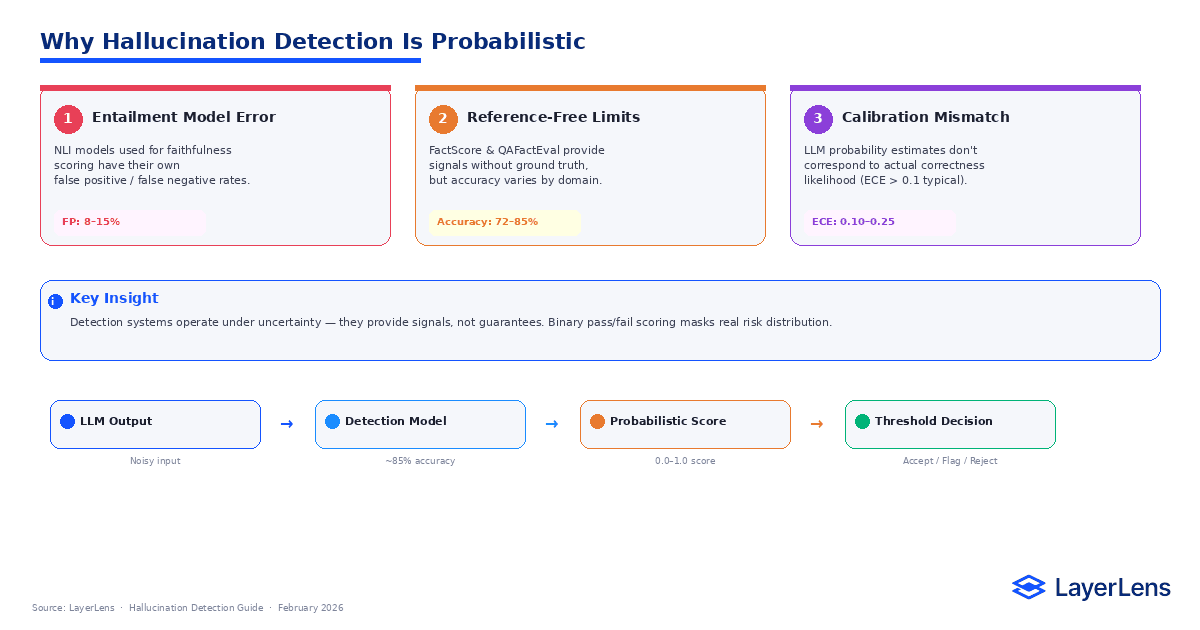
Why Is Hallucination Detection Probabilistic?
Hallucination detection relies on secondary scoring systems. These systems introduce their own error rates.
Faithfulness scoring frequently uses natural language inference models to test whether an answer is entailed by its context. These entailment models are themselves imperfect.
Reference-free factuality metrics such as FactScore (FactScore research: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14251) provide additional signals but cannot guarantee correctness without ground truth.
Confidence calibration compounds the problem. Neural networks are often miscalibrated, meaning confidence estimates do not align cleanly with empirical accuracy (Calibration research: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.04599).
LLM hallucination detection therefore produces risk scores, not certainty guarantees.
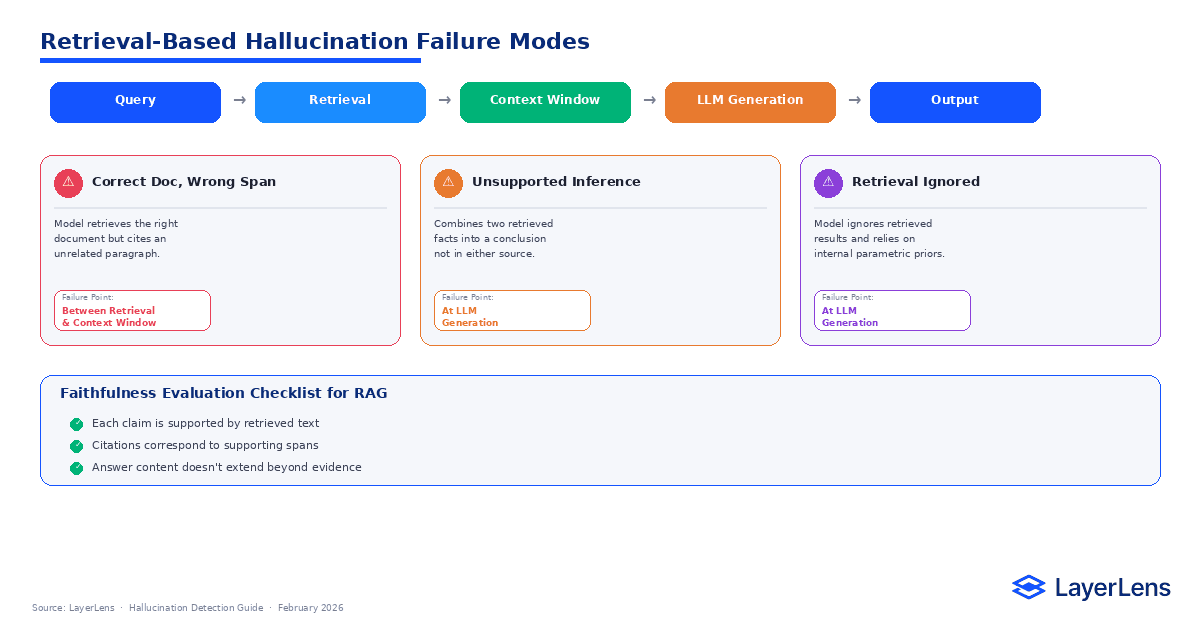
How Does RAG Affect LLM Hallucination Detection?
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) reduces fabrication risk by grounding outputs in external documents. It introduces new hallucination surfaces.
A model may retrieve correct documents yet cite unsupported spans. It may merge multiple retrieved facts into an unsupported inference. It may ignore retrieved context entirely.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation research (https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) highlights how grounding reduces but does not eliminate hallucination.
Detection in RAG systems must evaluate:
Whether each claim is supported by retrieved text
Whether citations correspond to supporting spans
Whether output extends beyond retrieval evidence
LayerLens benchmark coverage includes faithfulness and grounding benchmarks for structured evaluation (LayerLens benchmark coverage: https://app.layerlens.ai/benchmarks).
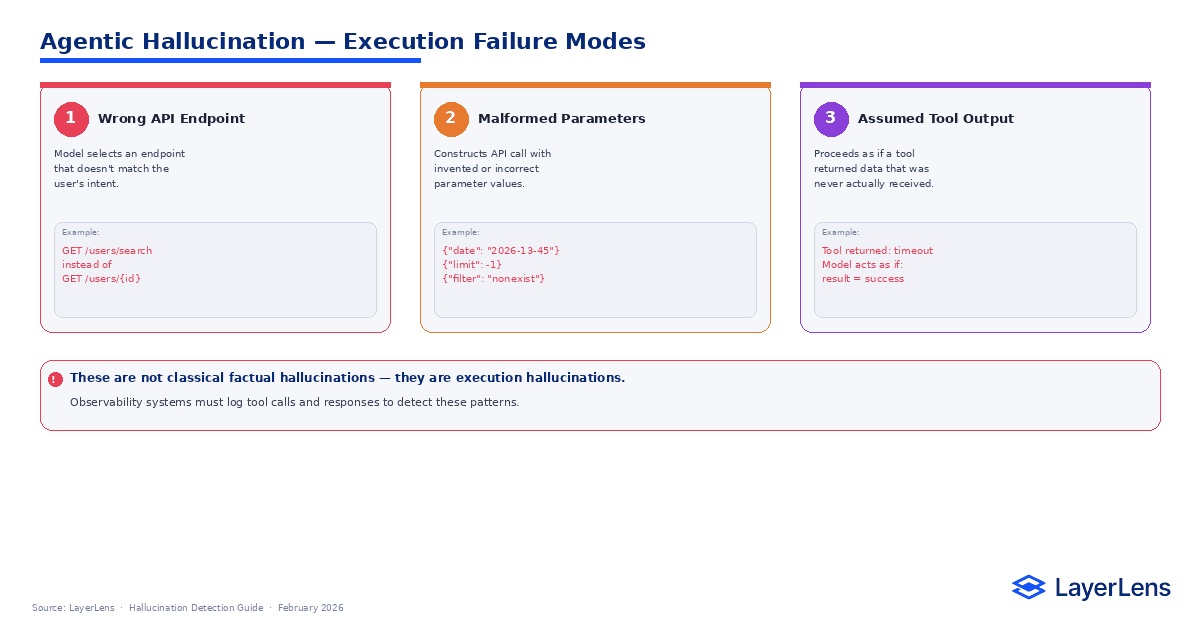
What Are Agentic Hallucinations in LLM Systems?
gentic systems introduce execution-level hallucination risk.
Examples include:
Selecting the wrong API endpoint
Passing malformed tool parameters
Assuming tool outputs that were never returned
Executing multi-step plans with unsupported intermediate assumptions
These are not purely factual hallucinations. They are reasoning-to-action hallucinations.
Runtime observability is required to detect them (LLM observability and runtime monitoring: https://layerlens.ai/blog/llm-observability).
For adversarial stress testing of these behaviors, see AI red teaming for LLMs (https://layerlens.ai/blog/ai-red-teaming-llm).
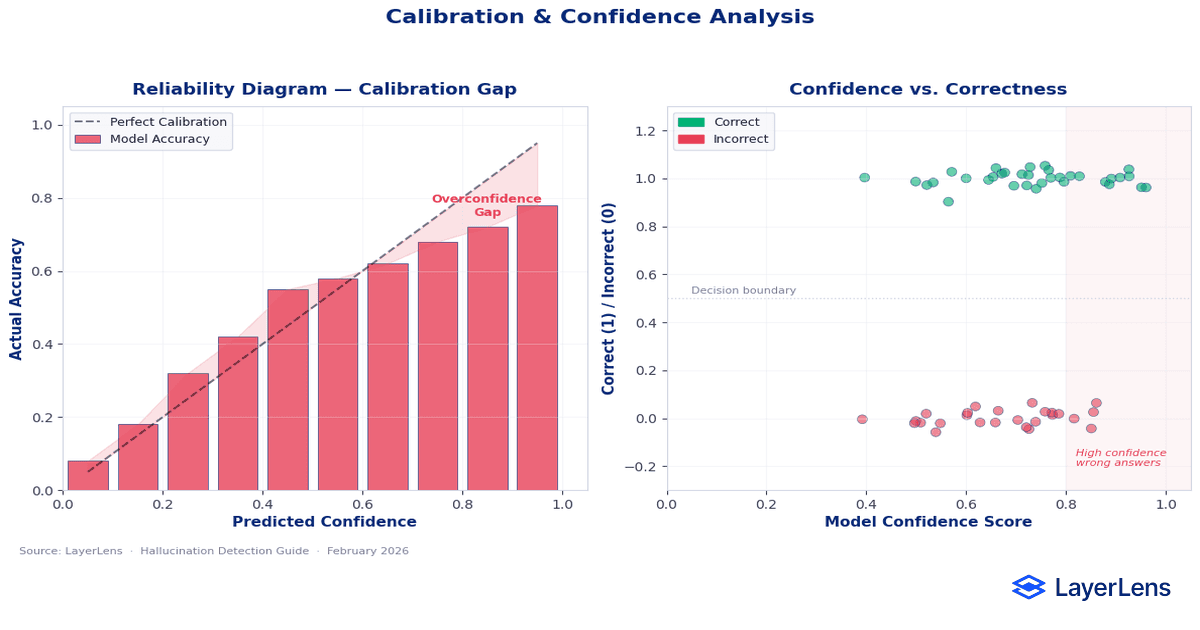
How Does Confidence Calibration Affect Detection?
Confidence is often mistaken for correctness.
Models frequently produce fluent, high-confidence language even when incorrect. Calibration research demonstrates misalignment between predicted probabilities and actual accuracy (Calibration research: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.04599).
Effective hallucination detection systems track:
Confidence scores
Entailment probabilities
Refusal rates
Variance across repeated runs
Overconfident wrong answers represent higher operational risk than uncertain ones.
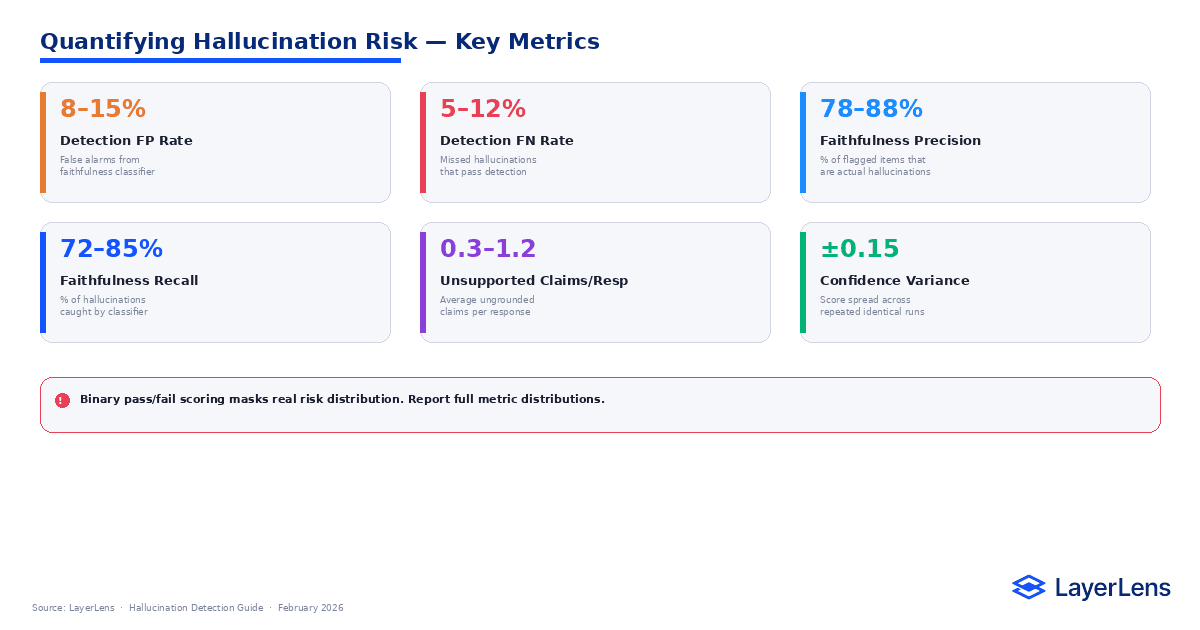
How Do You Quantify LLM Hallucination Risk?
Quantification should extend beyond binary labels.
Metrics include:
False positive and false negative rates of detection models
Precision and recall of faithfulness classifiers
Unsupported claim frequency per response
Confidence variance
Regression trends across model versions
These metrics should integrate with deployment gating logic (LLM evaluation framework: https://layerlens.ai/blog/llm-evaluation-framework).
Hallucination risk is better modeled as a distribution than as a pass/fail flag.
What Are Effective AI Hallucination Mitigation Methods?
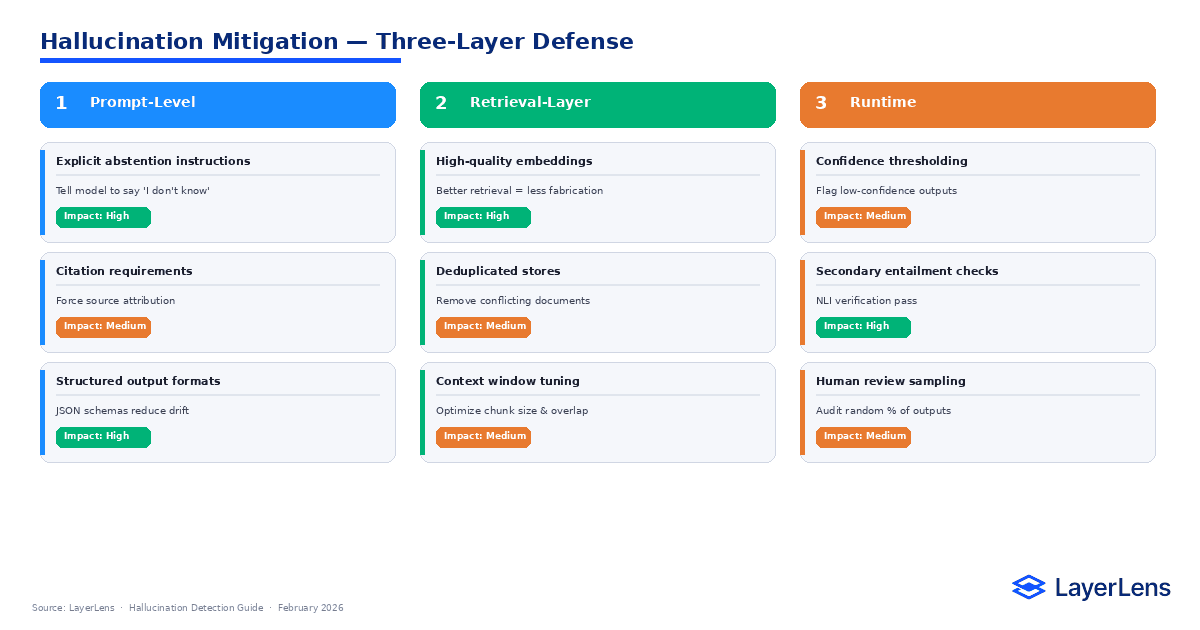
Mitigation is layered.
Prompt-Level Mitigation
Explicit abstention instructions
Citation requirements
Structured output constraints
Retrieval-Layer Mitigation
Embedding quality improvement
Context deduplication
Retrieval window tuning
Runtime Mitigation
Confidence thresholding
Secondary entailment checks
Human-in-the-loop sampling
AI hallucination mitigation should combine these layers rather than relying on a single method.
What Tools Detect LLM Hallucinations in Production?
LLM hallucination detection tools fall into three categories:
Evaluation platforms
LayerLens benchmark evaluation and faithfulness tracking (LayerLens evaluation dashboards: https://app.layerlens.ai/evaluations)
Research-based scoring systems
FactScore (https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14251)
Entailment-based scoring models
Runtime monitoring systems
Structured observability pipelines (LLM observability: https://layerlens.ai/blog/llm-observability)
Effective detection combines evaluation datasets, runtime signals, and mitigation workflows.
Conclusion
LLM hallucination detection in production systems is not about eliminating fabrication entirely. It is about bounding risk within operational thresholds.
Fabrication, misattribution, citation drift, speculative completion, and agentic execution errors require distinct detection logic. Faithfulness scoring reduces unsupported claims but introduces calibration tradeoffs. Retrieval reduces fabrication but introduces citation drift. Agentic systems introduce execution-level hallucinations.
Production hallucination management requires benchmarking, runtime observability, structured mitigation, and governance thresholds.
The objective is not certainty. It is controlled uncertainty that can be monitored, measured, and managed.
Key Takeaways
LLM hallucination detection is multi-surface and probabilistic.
Faithfulness scoring and entailment models reduce but do not eliminate risk.
Retrieval and agentic systems expand hallucination types.
Confidence calibration materially affects detection reliability.
Combining evaluation, observability, and mitigation reduces operational exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is LLM hallucination detection?
LLM hallucination detection identifies unsupported or fabricated claims in model outputs, including fabrication, citation drift, and speculative completion.
How does hallucination detection work?
It uses faithfulness scoring, entailment models, reference-free factuality metrics, and runtime observability to assess unsupported claims.
Why is hallucination detection probabilistic?
Detection models have error rates, and confidence calibration is imperfect (Calibration research: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.04599).
How does RAG affect hallucination detection?
RAG reduces fabrication by grounding outputs in retrieved documents but introduces citation drift and retrieval-specific errors (Retrieval-Augmented Generation research: https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401).
What tools detect LLM hallucinations in production?
Tools include benchmark evaluation platforms, faithfulness scoring systems, runtime observability dashboards, and structured mitigation pipelines.