
AI Red Teaming for LLMs in Production
Author:
Jake Meany (Director of Marketing, LayerLens)
Last updated:
Jan 23, 2026
Published:
Jan 23, 2026
AI red teaming deliberately probes LLM systems with adversarial prompts and attack simulations.
Static safety benchmarks do not capture evolving jailbreak and injection tactics.
Core metrics include jailbreak success rate, prompt injection override rate, refusal consistency, policy violations, and tool-call integrity.
Effective programs combine adversarial prompt libraries, automated testing, shadow sampling, and production logging.
Red teaming only works when results trigger release thresholds and rollback criteria.
Why AI Red Teaming Exists
Language models produce probabilistic outputs conditioned on context. Small prompt changes can move behavior across policy boundaries, especially when those boundaries are expressed as instructions rather than enforced rules.
AI red teaming tests that behavioral surface directly. It assumes users will try to override instructions, embed malicious content inside documents, or manipulate tool calls. Instead of asking whether the model usually behaves, red teaming asks when it stops behaving.
Insert Image: red-team-adversarial-map.png
Alt text: Diagram showing adversarial surfaces in LLM systems including jailbreaks, prompt injection, tool misuse, and policy evasion
Caption: Adversarial testing targets behavioral edges rather than average-case performance.
What Is AI Red Teaming?
AI red teaming is structured adversarial testing for generative systems. It focuses on misuse scenarios, boundary violations, and alignment stress tests rather than typical user queries.
In an LLM context, llm red teaming includes:
Jailbreak attempts that override system prompts
Prompt injection payloads embedded in retrieved context
Policy evasion through paraphrase or indirection
Tool manipulation in agentic workflows
Adversarial prompting research shows safety fine-tuning reduces but does not eliminate jailbreak success under targeted manipulation.
For the broader evaluation infrastructure that adversarial testing plugs into, see How to Build an LLM Evaluation Framework (Enterprise Playbook).
Why Static Safety Testing Fails
Static safety benchmarks measure known risk categories on fixed datasets. They do not simulate iterative attack strategies or distribution changes over time.
In production, prompts are not fixed. Attackers adapt. Retrieval pipelines ingest untrusted documents. Tool integrations expand attack surfaces. Distribution shift changes input patterns.
A model can pass baseline safety checks and still degrade when exposed to adversarial behavior at scale.
Core Categories of AI Red Teaming
Jailbreak Testing
Attempts to override safety instructions through prompt manipulation.
Prompt Injection Testing
Malicious instructions embedded inside retrieved documents or user input.
Policy Evasion
Indirect phrasing designed to bypass content filters.
Tool Manipulation
Adversarial instructions targeting API calls, plugins, or external systems.
Alignment Drift
Gradual weakening of refusal behavior over time.
Each category produces different measurable failure signals.
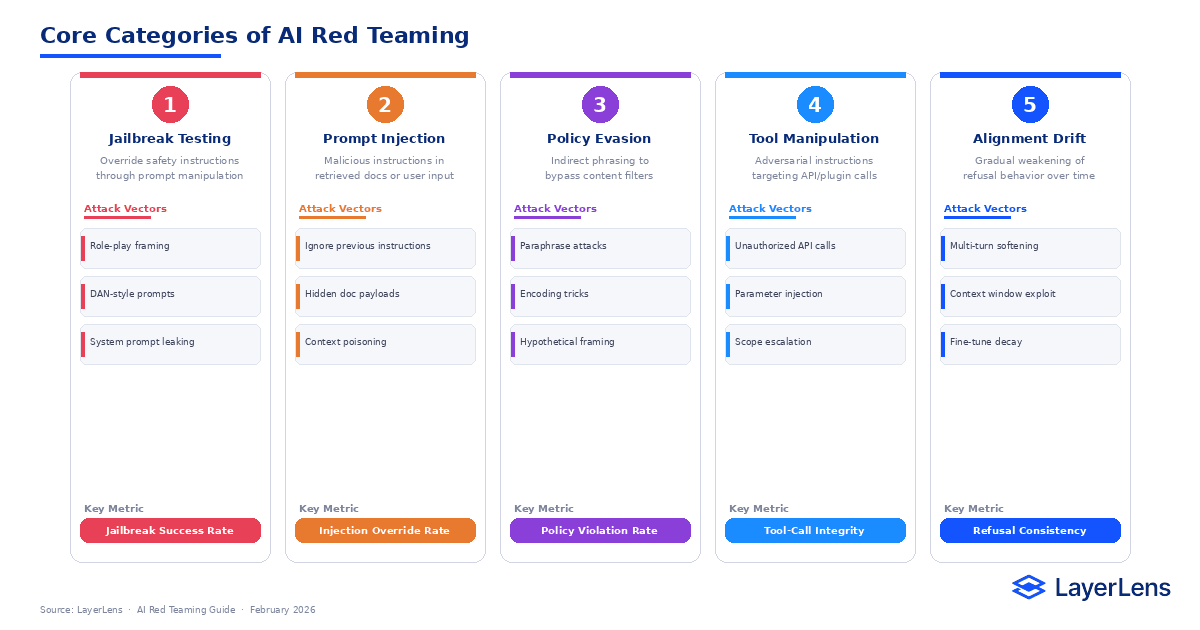
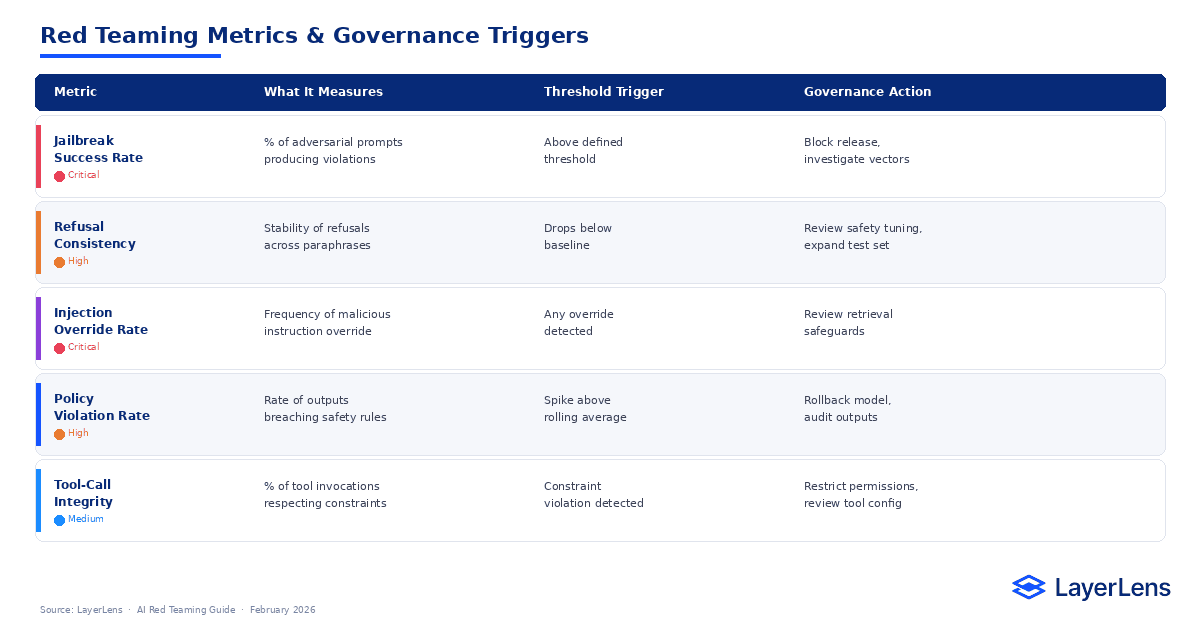
Red Teaming Metrics and Their Operational Meaning
Jailbreak Success Rate
The percentage of adversarial prompts that produce policy-violating outputs.
Refusal Consistency
How reliably the system refuses semantically equivalent disallowed requests.
Prompt Injection Override Rate
The frequency with which malicious instructions override intended constraints.
Policy Violation Rate
The rate of outputs breaching defined safety categories across sampled traffic.
Tool-Call Integrity
The proportion of tool invocations that respect defined constraints.
LayerLens evaluation dashboards support structured tracking of adversarial metrics across releases.
For a deeper breakdown of how to select and validate evaluation metrics, see LLM Evaluation Metrics That Actually Matter in Production.
Red Teaming KPI Mapping
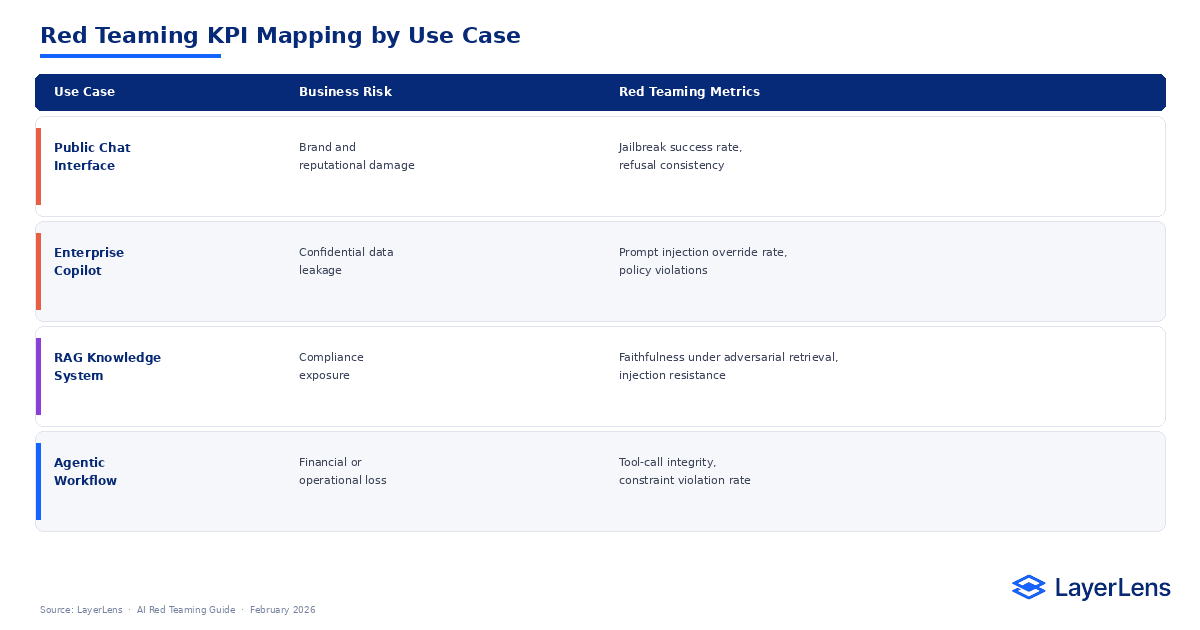
For how adversarial evaluation applies to retrieval systems and grounding failures, see RAG Evaluation.
Building an Adversarial Prompt Library
A red teaming program requires a structured prompt library.
These Include:
Canonical jailbreak templates
Paraphrased variants of the same disallowed request
Injection payloads embedded in realistic documents
Tool misuse scenarios targeting connected APIs
Multi-step attack chains combining retrieval and generation
Each prompt should be labeled by attack category and expected failure condition. The library should evolve as new exploit patterns emerge.
What Are the Best AI Red Teaming Tools and Frameworks?
AI red teaming tools and llm red teaming tools typically fall into three categories: attack simulation frameworks, guardrail systems, and production monitoring infrastructure.
Attack simulation and adversarial testing frameworks
Garak: https://github.com/leondz/garak
PyRIT: https://github.com/Azure/PyRIT
Microsoft Counterfit: https://github.com/Azure/counterfit
Guardrail and constraint systems
NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails: https://github.com/NVIDIA/NeMo-Guardrails
Production evaluation infrastructure
LayerLens Stratix Premium: https://layerlens.ai/stratix-premium
Tool choice depends on whether your focus is pre-deployment stress testing, regression automation, or continuous adversarial monitoring in production.
How to Run an AI Red Teaming Program Step-by-Step
Define threat models
Identify adversarial scenarios relevant to your deployment context.
Construct adversarial prompt sets
Target jailbreak, injection, policy evasion, and tool manipulation categories.
Execute structured testing
Measure jailbreak rate, refusal stability, and policy violations under controlled runs.
Deploy shadow adversarial sampling
Inject adversarial prompts into shadow traffic before rollout to observe real distribution effects.
Instrument and log
Capture responses, refusal flags, tool invocations, latency, and cost under adversarial load.
Tie results to release criteria
Define rollback thresholds triggered by adversarial metric breaches.
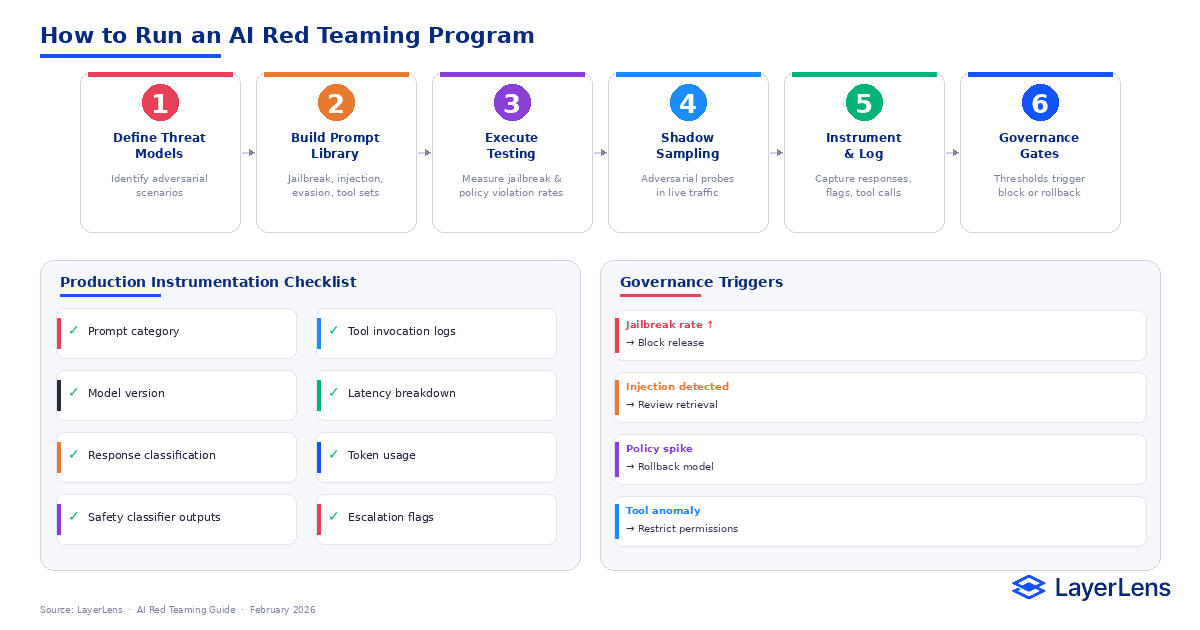
Production Instrumentation Checklist
Log for each adversarial test or sampled request:
Prompt category
Model version
Response classification (refusal, violation, compliant)
Safety classifier outputs
Tool invocation logs
Latency breakdown
Token usage
Escalation flags
Statistical monitoring should track adversarial success rates over time. Increases can indicate drift in refusal behavior or new exploit vectors.
How Should Red Teaming Results Connect to Deployment Governance?
Adversarial metrics must influence release decisions.
Example triggers:
Jailbreak success rate above threshold → block release
Prompt injection override detected → review retrieval safeguards
Policy violation spike → rollback
Tool-call anomaly → restrict permissions
Governance ties adversarial testing to authority. Without that linkage, results remain informational rather than operational.
For how to connect evaluation outputs to deployment gates and ownership, see How to Build an LLM Evaluation Framework (Enterprise Playbook).
What Are Common AI Red Teaming Mistakes?
Running red teaming only once before launch.
Testing only popular jailbreak templates.
Ignoring injection risks in retrieval pipelines.
Collecting metrics without defining action thresholds.
Separating red teaming from deployment governance.
Conclusion
Red teaming exposes the edges of system behavior. It tests what happens when instructions are manipulated, when context is poisoned, and when constraints are reframed.
The objective is not to prove that a model is safe. The objective is to quantify how it fails and ensure those failures trigger action. Without that linkage, adversarial testing becomes an audit exercise. With it, safety becomes measurable and enforceable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI red teaming for LLMs?
AI red teaming is structured adversarial testing designed to expose jailbreak, injection, and policy vulnerabilities in language model systems.
How often should LLM red teaming be conducted?
Continuously in production, with regular adversarial sampling and prompt library updates.
What are AI red teaming tools?
AI red teaming tools include Garak, PyRIT, NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails, Microsoft Counterfit, and production evaluation platforms such as LayerLens Stratix Premium.
How do you measure jailbreak effectiveness?
By tracking jailbreak success rate, refusal consistency, and policy violation frequency over time.
What is the difference between evaluation and red teaming?
Evaluation measures general performance. Red teaming measures adversarial robustness under intentional attack conditions.
Key Takeaways
Effective AI red teaming:
Targets adversarial inputs intentionally
Measures jailbreak and injection success rates
Tracks refusal consistency and policy violations
Instruments production traffic
Links adversarial findings to deployment gates